Our Services
Gum diseases and Treatment
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the tissues that surround and support the teeth. It is typically caused by poor oral hygiene, which allows bacteria in dental plaque to accumulate and inflame the gums. Early-stage gum disease is called gingivitis and is characterized by swollen, red gums that may bleed easily. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, which involves damage to the tissues and bone supporting the teeth. Regular brushing, flossing, and professional dental cleanings are essential for preventing gum disease. If you suspect you have gum disease, it's important to see a dentist for an evaluation and appropriate treatment.
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to thoroughly clean the pockets around teeth and prevent damage to surrounding gum tissue and bone. You have the best chance for successful treatment when you also have a daily routine of good oral care, manage health conditions that may impact dental health and stop tobacco use.
Nonsurgical Treatments
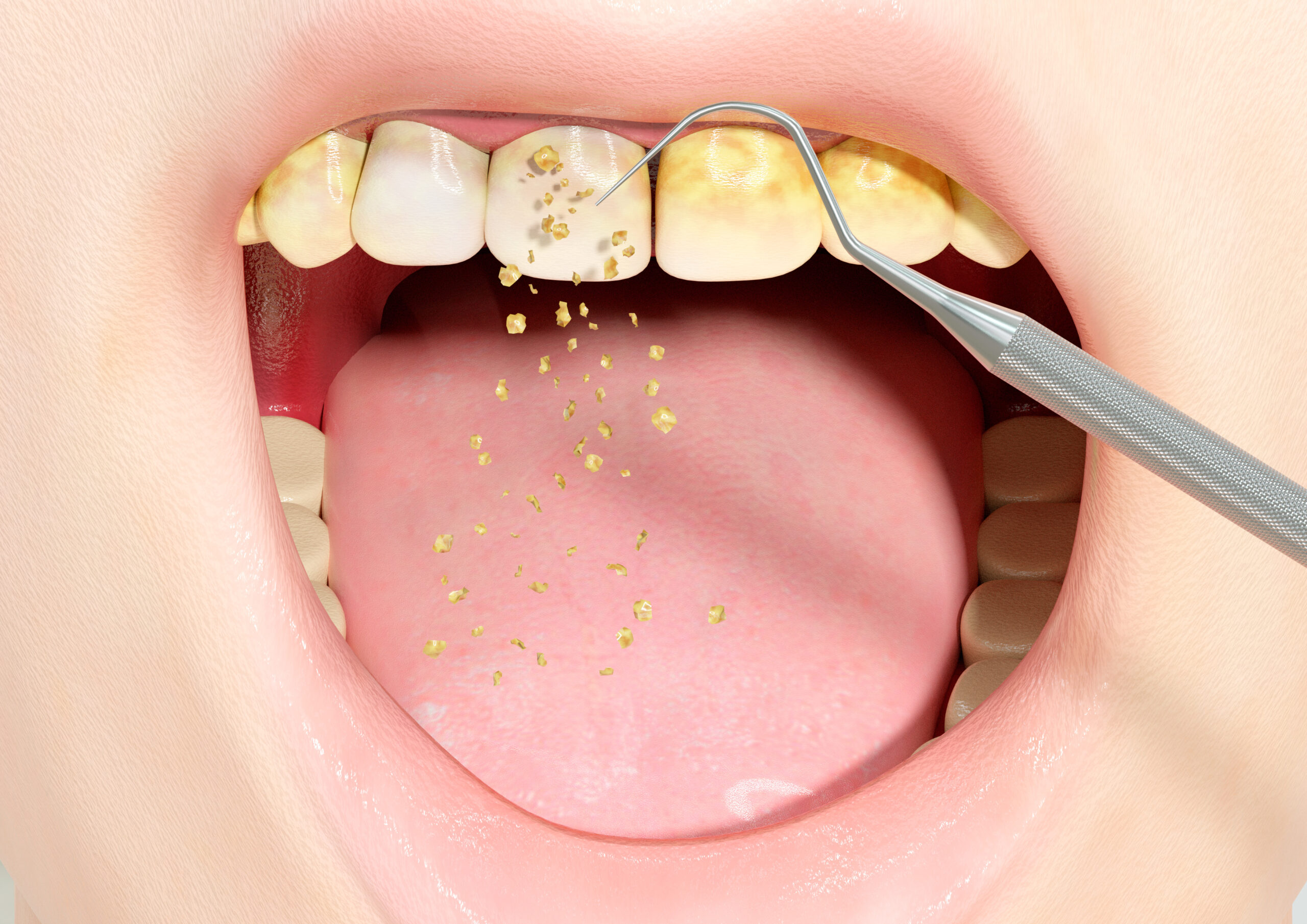
Scaling: Scaling removes tartar and bacteria from your tooth surfaces and below your gumline. It may be done using instruments, a laser or an ultrasonic device.
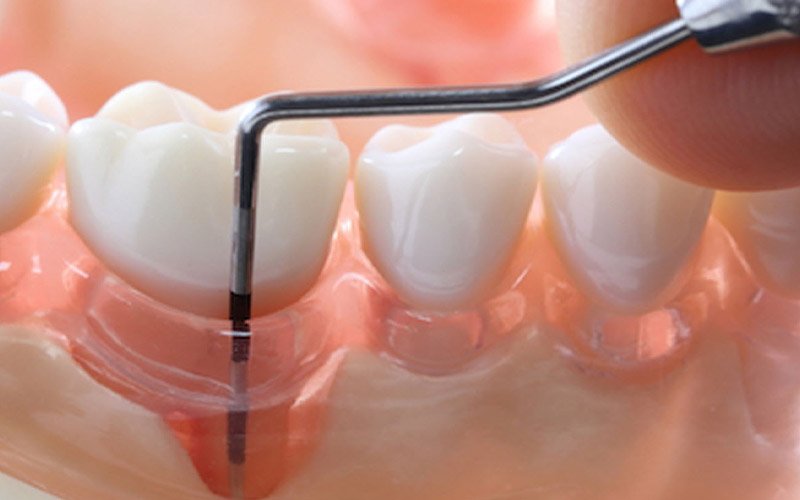
Root planing: Root planing smooths the root surfaces. This helps prevent further buildup of tartar and bacteria. It also helps your gums attach to your teeth again.
Antibiotics: Topical or oral antibiotics can help control bacterial infection. Topical antibiotics can include antibiotic mouth rinses or putting gel containing an antibiotic into gum pockets. Sometimes oral antibiotics are needed to get of bacteria that cause infections.
Surgical Treatments
Flap surgery, also called pocket reduction surgery: Your periodontist makes cuts in your gums to carefully fold back the tissue. This exposes the tooth roots for more effective scaling and root planing. Because periodontitis often causes bone loss, the underlying bone may be reshaped before the gum tissue is stitched back in place. After you heal, it's easier to clean the areas around your teeth and maintain healthy gum tissue.
Soft tissue grafts: When you lose gum tissue, your gumline gets lower, exposing some of your tooth roots. You may need to have some of the damaged tissue reinforced. This is usually done by removing a small amount of tissue from the roof of your mouth or using tissue from another donor source and attaching it to the affected site. This can help reduce further gum loss, cover exposed roots and give your teeth a better appearance.
Bone grafting: This procedure is performed when periodontitis destroys the bone around your tooth root. The graft may be made from small bits of your own bone, or the bone may be made of artificial material or donated. The bone graft helps prevent tooth loss by holding your tooth in place. It also serves as a platform for the regrowth of natural bone.